

Tongue cancer is a form of cancer that begins in the cells of the tongue.
Several types of cancer can affect the tongue, but tongue cancer most often begins in the thin, flat squamous cells that line the surface of the tongue. The type of cells involved in your tongue cancer helps determine your prognosis and treatment.
Where your tongue cancer occurs also affects your treatment. Tongue cancer can occur:
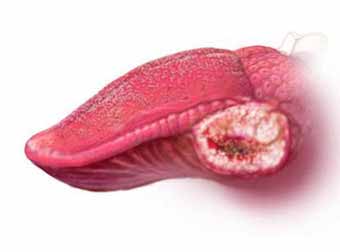
Treatment for tongue cancer typically involves surgery to remove the cancer. Chemotherapy, radiation therapy and targeted drug therapy also may be recommended.